NASA drills freaky scenario where elusive asteroid heads towards Earth
What if,关键字2 in 14 years, a newly-discovered asteroid was likely to strike Earth?
But that's not all.This threatening space rock, some 330 to 1,050 feet in diameter (or 100 to 320 meters), has just disappeared behind the sun, making crucial observations impossible for the next seven months.
To prepare for such an unsettling scenario, NASA just completed an exercise to "inform and assess our ability as a nation to respond effectively to the threat of a potentially hazardous asteroid or comet." A possible asteroid or comet collision can pose a number of uncertainties, which the space agency continued to test during the recent fifth Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise.
You May Also Like
"A large asteroid impact is potentially the only natural disaster humanity has the technology to predict years in advance and take action to prevent," Lindley Johnson, NASA's planetary defense officer emeritus, said in a statement.
SEE ALSO: NASA scientist viewed first Voyager images. What he saw gave him chills.Importantly, there are no known asteroids on a collision course with Earth for at least 100 years, and the chances of a major impact in our lifetimes is extremely small, astronomers say. Planetary defense agencies have never needed to raise an alarm about a threatening impact — though you've undoubtedly seen sensationalized news about menacing asteroids over the years.
"We have never actually issued a warning," Johnson previously told Mashable. (But they have informed the public about what some asteroids of interest are doing.)
"We have never actually issued a warning."
But, at some point, an impact is inevitable. "Yes, asteroids have hit Earth over the course of its history, and it will happen again," NASA notes.
In the latest asteroid collision scenario, the space agency presented a hypothetical object some 330 to 1,050 feet across that has a 72 percent chance of walloping Earth. Something in that range, while not nearly the biggest class of asteroid, could be hugely destructive. Take the 600-foot-deep "Meteor Crater," which landed in present-day Arizona 50,000 years ago. The culprit was likely some 100 to 170 feet across, but created a blast big enough to destroy Kansas City.
As the hypothetical trajectory below shows, this asteroid passes over some densely populated areas like Dallas, which would almost certainly create a national emergency, even if the exact trajectory is uncertain. The scenario's impact is expected in 14 years, in July 2038, giving countries a relatively short time to prepare — especially with a seven month gap in surveillance. From initial observations, the object's size, composition, and trajectory are uncertain.
"To complicate this year’s hypothetical scenario, essential follow-up observations would have to be delayed for at least seven months — a critical loss of time — as the asteroid passed behind the Sun as seen from Earth’s vantage point in space," the space agency said.
 A hypothetical asteroid impact scenario created for the Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise. Credit: NASA
A hypothetical asteroid impact scenario created for the Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise. Credit: NASA  A slide from the Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise showing courses of action for contending with a likely impact. Credit: Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise
A slide from the Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise showing courses of action for contending with a likely impact. Credit: Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise This latest planetary defense exercise underscores how critical near-Earth object surveillance is (these are objects that come within some 30 million miles of Earth's orbit around the sun). Fourteen years is a rushed timeline.
"You need to know what's coming, when it's coming, and how hard it's going to hit," Eric Christensen, the director of the NEO-seeking Catalina Sky Survey in Arizona, previously told Mashable.
Related Stories
- NASA spacecraft spots dead robot on Mars surface
- Astronomers just witnessed a whole galaxy 'turn on the lights' in real-time
- The best telescopes for gazing at stars and solar eclipses in 2024
- The mega-comet hurtling through our solar system is 85, yes 85, miles wide
- The first images of Earth are chilling
"You need to know what's coming, when it's coming, and how hard it's going to hit."
Among the courses of action discussed by NASA, FEMA, and other partners included a flyby of the incoming object, which would vastly improve our grasp of its composition, rotation, speed, and beyond. Will it break apart into smaller pieces in Earth's atmosphere? Is it rubble-like, or solid? How likely is it to hit the ocean? Also discussed was the major operation, a "Purpose-Built Rendezvous," which implies using a spacecraft to deflect an object.
Asteroid deflection is a realistic future possibility. In 2022, NASA plunged a refrigerator-sized spacecraft into a stadium-sized asteroid, with hopes of simply nudgingit. It was an unprecedented, successful test — proving humanity could alter the path of a menacing asteroid, should one ever be headed our way. The impact cut the asteroid Dimorphos' loop around its parent asteroid (they journey around the sun as a pair, or binary system) by a whopping 33 minutes and 15 seconds — when the original goal was to change it by at least 73 seconds.
 Participants at the fifth Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise. Credit: NASA / JHU-APL / Ed Whitman
Participants at the fifth Planetary Defense Interagency Tabletop Exercise. Credit: NASA / JHU-APL / Ed Whitman Ultimately, this latest tabletop impact exercise resulted in a number of "High-level Takeaways." A glaring problem is the uncertainties involved in planning for a likely impact. The participants recommended developing "the capability to rapidly launch an NEO [near-Earth object] reconnaissance mission," which could include repurposing existing spacecraft.
Thankfully, NASA and its planetary defense partners will continue exercising hypothetical asteroid threats. It behooves us to be prepared, even if the overall risk is low.
The risks of an asteroid impact
Here are today's general risks from asteroids or comets both tiny, and very large. (Importantly, even relatively small rocks are still threatening, as the surprise 56-foot (17-meter) rock that exploded over Russia and blew out people's windows in 2013, proved.
Every single day about 100 tons of dust and sand-sized particles fall through Earth's atmosphere and promptly burn up.
Every year, on average, an "automobile-sized asteroid" plummets through our sky and explodes, explains NASA.
Impacts by objects around 460 feet in diameter occur every 10,000 to 20,000 years.
A "dinosaur-killing" impact from a rock perhaps a half-mile across or larger happens on 100-million-year timescales.
(责任编辑:剑破天门)
-
 近日,网传“8岁女孩遭男孩长期霸凌”的视频引发公众关注。浙江省淳安县组织县教育局、县公安局、威坪镇等相关单位成立联合调查组,对相关情况进行调查核实。今天6月7日),@淳安发布 发布通报。通报称,经查,
...[详细]
近日,网传“8岁女孩遭男孩长期霸凌”的视频引发公众关注。浙江省淳安县组织县教育局、县公安局、威坪镇等相关单位成立联合调查组,对相关情况进行调查核实。今天6月7日),@淳安发布 发布通报。通报称,经查,
...[详细]
-
北京市教委:秋季学期起义务教育学校学生课间10分钟延长至15分钟
 8月30日,记者从北京市教委了解到,从今年秋季学期起,北京市义务教育学校将对课间安排做出整体统筹优化,原则上落实15分钟课间时长,提供更加从容的课间时间,引导师生走出教室、走向户外、走进阳光,享受更加
...[详细]
8月30日,记者从北京市教委了解到,从今年秋季学期起,北京市义务教育学校将对课间安排做出整体统筹优化,原则上落实15分钟课间时长,提供更加从容的课间时间,引导师生走出教室、走向户外、走进阳光,享受更加
...[详细]
-
รพ.พระนั่งเกล้า แถลงกรณีพยาบาลโดนทำร้ายขณะปฏิบัติหน้าที่
 แถลงการณ์โรงพยาบาลพระนั่งเกล้า เรื่องเหตุการณ์ความรุนแรงต่อบุคลากรทางการแพทย์โรงพยาบาลพระนั่งเกล้าขอ
...[详细]
แถลงการณ์โรงพยาบาลพระนั่งเกล้า เรื่องเหตุการณ์ความรุนแรงต่อบุคลากรทางการแพทย์โรงพยาบาลพระนั่งเกล้าขอ
...[详细]
-
 北京 2025年6月9日 /美通社/ -- 日产汽车公司近期发布了2024财年财报2024年4月至2025年3月),同时发布了"Re:Nissan"重振日产)战略计划,旨在通过一系
...[详细]
北京 2025年6月9日 /美通社/ -- 日产汽车公司近期发布了2024财年财报2024年4月至2025年3月),同时发布了"Re:Nissan"重振日产)战略计划,旨在通过一系
...[详细]
-
 在1.95神龙合击中有同伙说双战组合是最壮大的组合,然则在我看来,全部的组合或多或少都邑存在着一些烦恼,下面是我总结的一些经验,愿望可以或许对同伙们起到必定的感化。壮大的双战组合,我不否定这个组合确切
...[详细]
在1.95神龙合击中有同伙说双战组合是最壮大的组合,然则在我看来,全部的组合或多或少都邑存在着一些烦恼,下面是我总结的一些经验,愿望可以或许对同伙们起到必定的感化。壮大的双战组合,我不否定这个组合确切
...[详细]
-
 日期:2023/2/23 8:19:00作者:网友整理人气:0我来评论导读:体验过被重视的感觉,当自己不被的重视的时候是开心不起来了,也是很心酸难过的。 1.热情这东西耗尽了就只剩疲倦和冷漠
...[详细]
日期:2023/2/23 8:19:00作者:网友整理人气:0我来评论导读:体验过被重视的感觉,当自己不被的重视的时候是开心不起来了,也是很心酸难过的。 1.热情这东西耗尽了就只剩疲倦和冷漠
...[详细]
-
 日期:2023/2/23 8:19:00作者:网友整理人气:0我来评论导读:体验过被重视的感觉,当自己不被的重视的时候是开心不起来了,也是很心酸难过的。 1.热情这东西耗尽了就只剩疲倦和冷漠
...[详细]
日期:2023/2/23 8:19:00作者:网友整理人气:0我来评论导读:体验过被重视的感觉,当自己不被的重视的时候是开心不起来了,也是很心酸难过的。 1.热情这东西耗尽了就只剩疲倦和冷漠
...[详细]
-
UEFA Nations League livestream: How to watch Nations League for free
 TL;DR:Germany vs. France and Spain vs. Portugal are available to live stream for free. Access these
...[详细]
TL;DR:Germany vs. France and Spain vs. Portugal are available to live stream for free. Access these
...[详细]
-
 《斯普拉遁3》10.0.0版本更新引发意料之外的争议:Switch2玩家获得更流畅帧数、更清晰画质的同时,初代ns版本却遭到人为画质降级。随着硬件差距显现,任天堂做出艰难抉择——在“区域对战”“鱼虎对
...[详细]
《斯普拉遁3》10.0.0版本更新引发意料之外的争议:Switch2玩家获得更流畅帧数、更清晰画质的同时,初代ns版本却遭到人为画质降级。随着硬件差距显现,任天堂做出艰难抉择——在“区域对战”“鱼虎对
...[详细]
-
NYT Strands hints, answers for June 8
 If you're reading this, you're looking for a little help playing Strands, the New York Times' elevat
...[详细]
If you're reading this, you're looking for a little help playing Strands, the New York Times' elevat
...[详细]

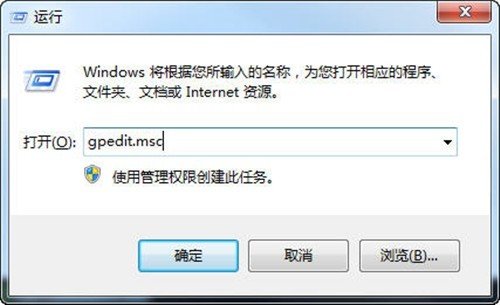 win 7系统不用网页时账号自动退出登录的设置办法
win 7系统不用网页时账号自动退出登录的设置办法 医师年度个人总结报告(范文5篇)
医师年度个人总结报告(范文5篇) 2021年北京冠军杯马术巡回赛收官站圆满结束
2021年北京冠军杯马术巡回赛收官站圆满结束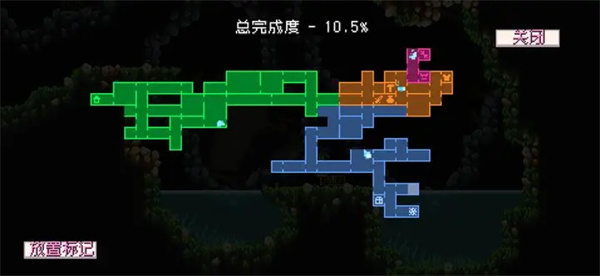 怪物乐土二段跳靴子获取位置分享
怪物乐土二段跳靴子获取位置分享
